Abstract
Key Points:
These data from a nationally representative sample of US adults with alcohol use disorders revealed a robust significant association of high symptom severity with access, continuation and discontinuation from Alcoholics Anonymous.
The association of high symptom severity and negative life events supports the behavioral economic model of AA access and continuation as proposed in this paper.
Variables associated with access to AA were also associated with continuation in AA, except for the variables for gender and education level. Women were less likely to attend AA, but more likely to continue attending. College educated respondents were less likely to attend AA, but more likely to continue attending.
A sub-group of US adults with severe externalizing disorders, identified in this study, are associated with access to and continuation in AA
In the US there is a a significant geographic regional variation in access to and continuation in AA
1. INTRODUCTION
This working paper provides an analysis of variables associated with access to AA prior to the past year and continuance in AA during the past year in a representative sample of DSM-IV alcohol abuse and alcohol dependent respondents in the United States .
Understanding the characteristics of persons with alcohol use disorders who did not attend AA, those who attended AA and those who dropped out may lead to improved AA referral and attendance.
This understanding may assist in providing appropriate encouragement for persons with alcohol use disorders who are in need of abstinence support but at a high risk for failing to seek support through AA membership.
The purpose of this study is to present and test a theoretical model of access to and continuance in AA.
-
Help-seeking associated with high severity and low efficacy/powerlessness. Carrillo’s[5]behavioral economic concept of abstinence as a second-best decision based on time-inconsistency (perceived severity) and Fiorentine and Hilhouse’s[6] Addicted-Self model, low self-efficacy associated with increase in abstinence acceptance.
-
Help-seeking associated with negative life events (social control hypothesis, change in consciousness due to increased sensitivity to other’s drinking behavior, Cahalan/Room[7] concept of intrapunitiveness) Value Expectancy theory emphasizing cognitive factors that are associated with motivation for behavior change.
-
Alcoholics Anonymous as a self-control commitment device [8] used by respondents, with high perceived severity of alcohol-related problems, to achieve and supporting abstinence
2. ANALYSIS
The descriptive statististics in this study are categorical data therefore the chi-square test is used to determine whether there is association between the categorical variables and access to and continuance in AA.
In this study the multiple categorical variables will collapsed to form 2 x 2 contingency tables to test the null hypothesis of no association.
For the purposes of this study the acceptance of the null hypothesis that there is no association is a P-value greater than 0.05.
3. METHODS
3.1 Sample
This study was based on the 1992 National Longitudinal Alcohol Epidemiologic Survey, sponsored by the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism data were collected via personal interviews onducted in respondents’ homes by US Bureau of the Census interviewers. The survey sample consisted of adults 18 years or older who were selected at random from a nationally representative sample of households.
3.2 Measures
3.2.1 Alcohol Use Disorders
Diagnoses of alcohol use disorders (AUD), as classified in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition (DSM-IV), were derived from the Alcohol Use Disorders and Associated Disabilities Interview Schedule, a fully structured psychiatric interview designed to be administered by trained lay interviewers[9]
The interview schedule included an extensive list of symptom items that operationalized the DSM-IV criteria for alcohol abuse and dependence. Respondents were classified with past year dependence if they met at least 3 of the 7 DSM-IV criteria for dependence within the 1-year period preceding the interview: tolerance; withdrawal or avoidance of withdrawal; desire or attempts to cut down or stop drinking; much time spent on drinking, obtaining alcohol, or recovering from its effects; reduction/ cessation of important activities in favor of drinking; impaired control; and continue drinking despite physical or psychological problems caused or exacerbated by drinking. Respondents were classified with past-year alcohol abuse if they met at least 1 of the 4 DSM-IV criteria for abuse in the 1-year period preceding the interview: alcohol related legal problems, continued drinking despite interpersonal problems, neglect of role responsibilities as a result of drinking, and drinking in hazardous situations.
3.2.2 Alcoholics Anonymous Attendance
3.2.3 Severity Measure
High Severity
3.2.4 Negative Life Events
Mental Health Problems
Item 6168 “Have you ever had a mental or emotional problem”,
item 7170 “Have you ever seen anyone for a mental or emotional problem – a doctor, counselor, or any othe health professional?”.Item 7171 “Have you ever been a patient in any type of hospital or clinic overnight because of mental or emotional problems?”
Health Problems
Item 2244 “Did you ever have any health problem as a result of your drinking – like stomach or liver disease, memory problems, or pancreatits?”Item 2142 “Continue to drink even though you knew it was causing you a health problem or making a health problem worse?”Item 2217 ” Continue to drink even though you had a sertious health problem that might be made worse by drinking?”
School/job problems
Item 2224 Have job or school trouble because of your drinking – like missing too much work, not doing your work well, being demoted at work, or dropping out of school?”
Family problems
Item 2225 “Drift apart from a spouse, boyfriend/girlfriend, relative, or friend you cared about because of your drinking?”
Personal Accidents
Item 2243 ” Accidentally injure yourself while under the influence of alcohol, for example , have a bad fall or cut yourself badly, get hurt in a traffic accident, or anything else.”
Vehicle Accidents
Item 2226 “Have a car, notorcycle, truck, boat, or other accident becuse of your drinking?”
Arrests
Item 2227 “Get arrested or held at a police station because of your drinkig?”Fights
Fights
Item 2228 “Get into a physical fight while drinking or right after drinking?”
Driving problems
Item 2111 “Drive a car, motorcycle, truck, boat, or other vehicle after having too much to drink?”
Drug Use
Sedatives
Item 5104 Did you ever use sedatives, for example sleeping pills, barbituates, Seconal, Quaaludes, or Chloral Hydrate at least 12 times, on your own, before past year
Tranquilizers
Item 5123 Did you ever use tranquilizers or ant-anxiety drugs, for example Valium, Librium, muscle relaxants,or Xanax at least 12 times, on your own, before past year
Painkillers
Item 5142 Did you ever use painkillers, for example Codine, Darvon, Percodan, Dilaudid, or Demerol at least 12 times, on your own, before past year
Stimulants
Item 5161 Did you ever use stimulants, for example Preludin, benzadrine, methedrine, uppers, or speed at least 12 times, on your own, before past year
Marijuana
Item 5180 Did you ever use marijuana, hash, THC, or grass at least 12 times, on your own, before past year
Cocaine
Item 5199 Did you ever use cocaine or crack at least 12 times, on your own, before past year
Heroin
Item 5219 Did you ever use heroin at least 12 times, on your own, before past year
Methadone
Item 5234 Did you ever use methadone at least 12 times, on your own, before past year
Any Other Drug
Item 5251 or item 5268 Did you ever use other medicines, drugs or substances, for example, amyl nitrate, nitrous oxide, elavil, thorazine, or hallucinogens, such as LSD, mescaline, psilocybin, PCP, angel dust or peyote least 12 times, on your own, before past year
3.2.5 Socio-demographic Variables
Gender
1) Male2) Female
Age
1) 18-292) 30-393) 40-494) 50-595) 60+
Race
1) White2) Black3) American Indian/Alaskan Native4) Asian/Pacific Islanders
Marital Status
1) Married2) Cohabited3) Widowed4) Divorecd5) Separated6) Never married
Education
1) grade 7 or less2) grade 83) grade 9-114) grade 125) some college6) completed college
Employment Status
1) Employed2) Unemployed3 Retired4) In-school5) Full-time homemaker6) Other
Geographic Region
1) North-East2) Mid-West3) South4) West
Urban/Rural
1) Urban2) Rural
Age First Drinking
1) 14 years or younger2) 15 Years or older
4. RESULTS
-
high severity of diagnostic symptoms
-
prior-to-past year drug use
-
negative life events
-
male gender
-
age 30 years and older
-
divorced
-
lower education level, 12th grade or less
-
unemployed
-
mid-west and west geographic regions
- early age, 14 years or younger, of first drinking,
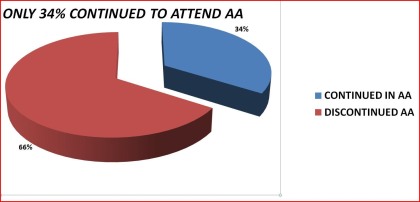
Only 34% of the respondents who attended AA prior to the past year continued to attend Alcoholics Anonymouis meeting during the past year. The analysis indicated that the following variables where associated with continuation in AA:
-
high severity of diagnostic symptoms,
-
mental health, health, school/job, and family problems
-
personal and vehicle accidents
-
female gender
-
divorced
-
higher education level, some college or higher
-
north-east and west geographic regions
-
urban population
-
early age, 14 years and younger, of first drinking
-
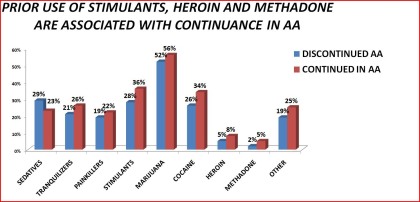
prior-to-past year stimulant, heroin, and methadone use
Access to Alcoholics Anonymous
Alcoholics Anonymous Attendance
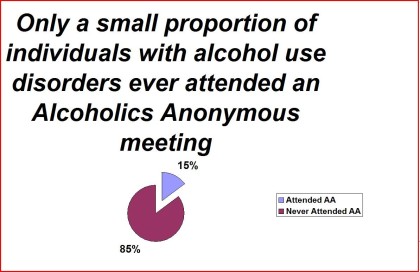
Table 1. Prior-to-past year DSM-IV alcohol abuse/dependence by access to Alcoholics Anonymous during the period prior to the past year: 1992 National Longitudinal Epidemiologic Survey
______________________________________________________________________N 5728
______________________________________________________________________
Never attend AA 85%
Attend AA 15%
______________________________________________________________________
Severity
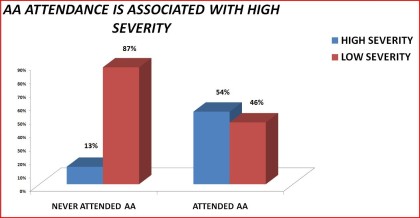
Table 2. Access to Alcoholics Anonymous by level of severity: 1992 National Longitudinal Alcohol Epidemiologic Survey
______________________________________________________________________Never Attended Ever Attended SignificanceAA AA Level_______________________________________________________________________N 4,861 867High Severity 13% 54% < .0001Low Severity 87% ` 46%______________________________________________________________________
Negative Life Events
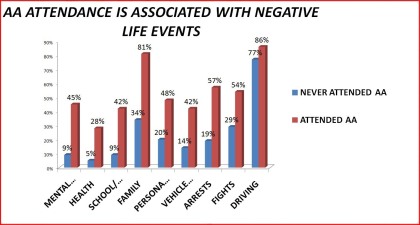
Table 3 Access to Alcoholics Anonymous by negative life events: 1992 National Longitudinal Alcohol Epidemiologic Survey
______________________________________________________________________Never Attended Ever Attended SignificanceAA AA Level_______________________________________________________________________N 4,831 860Mental Health Problems 9% 45% < .0001Health Problems 5% ` 28% < .0001School/Job Problems 9% 42% < .0001Family Problems 34% 81% < .0001Personal Accidenrts 20% 48% < .0001Vehicle Accidents 14% 42% < .0001Arrests 19% 57% < .0001Fights 29% 54% < .0001Driving Problems 77% 86% < .0001__________________________________________________________________________
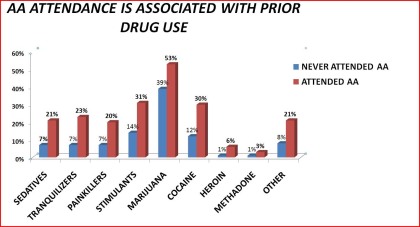
Prior-to past year drug use
Table 4. Access to Alcoholics Anonymous by prior-to-past year drug use: 1992 National Longitudinal Alcohol Epidemiologic Survey
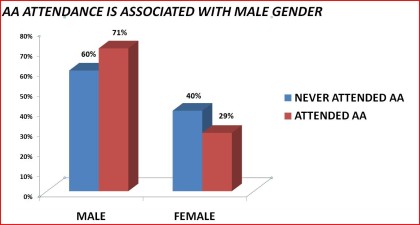
Gender
Table 5. Access to Alcoholics Anonymous by gender: 1992 National Longitudinal Alcohol Epidemiologic Survey
______________________________________________________________________Never Attended Ever Attended SignificanceAA AA Level_______________________________________________________________________N 4,861 867Male 60% 71% < .001Female 40% ` 29%
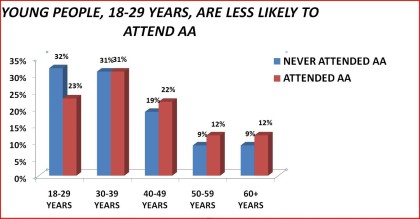
Age
Table 6. Access to Alcoholics Anonymous by age: 1992 National Longitudinal Alcohol Epidemiologic Survey
______________________________________________________________________Never Attended Ever Attended SignificanceAA AA Level_______________________________________________________________________N 4,861 86718-29 years 32% 23 %30-39 years 31% 31%40-49 years 19% ` 22%50-59 years 9% 12%60+ years 9% 12%________________________________________________________________________18-29 years 32% 23% < .00130+ years 68% 77%________________________________________________________________________
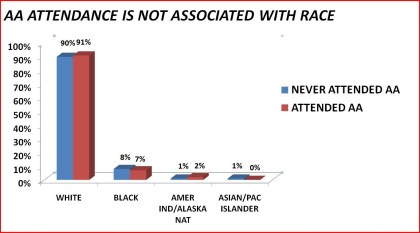
Race
Table 7. Access to Alcoholics Anonymous by race: 1992 National Longitudinal Alcohol Epidemiologic Survey
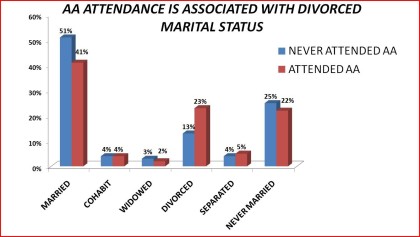
Marital Status
Table 8. Access to Alcoholics Anonymous by marital status: 1992 National Longitudinal Alcohol Epidemiologic Survey
______________________________________________________________________
Never Attended Ever Attended Significance
AA AA Level
______________________________________________________________________
N 4,824 863
Married 51% 41 %
Cohabit 4% 4%
Widowed 3% ` 2%
Divorced 13% 23%
Separated 4% 5%
Never Married 25% 22%
____________________________________________________________________
Education
Table 9. Access to Alcoholics Anonymous by education: 1992 National Longitudinal Alcohol Epidemiologic Survey
______________________________________________________________________
Never Attended Ever Attended Significance
AA AA Level______________________________________________________________________
N 4,821 857
Grade 7 or less 2% 2%
Grade 8 2% 2%
Grade 9-11 10% 14%
Grade 12 28% 33%
Some College 31% 30%
Completed College 27% 19%
____________________________________________________________________________
Grade 12 or less 42% 52% < .0001
Some College or more 58% 48%
_______________________________________________________________________________
Employment Status
Table 10. Access to Alcoholics Anonymous by employment status: 1992 National Longitudinal Alcohol Epidemiologic Suvey
______________________________________________________________________
Never Attended Ever Attended Significance
AA AA Level
______________________________________________________________________
N 4,789 845
Age of First Use of Alcohol
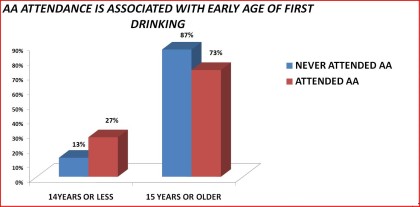 |
|
Figure 11. AA attendance by age of first use of alcohol
|
Table 11. Access to Alcoholics Anonymous by age of first use of alcohol: 1992 National Longitudinal Alcohol Epidemiologic Suvey
______________________________________________________________________
Never Attended Ever Attended Significance
AA AA Level
______________________________________________________________________
N 4,819 864
14 years or less 13% 27% < .0001
15 years and older 87% 73%
__________________________________________________________________________________
Geographic Region
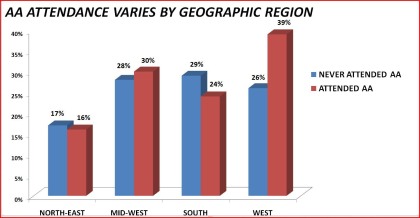 |
|
Fighure 12. AA attendance by geographic region
|
Table 12. Access to Alcoholics Anonymous by geographic region of United States: 1992 National Longitudinal Alcohol Epidemiologic Suvey
______________________________________________________________________
Never Attended Ever Attended Significance
AA AA Level
______________________________________________________________________
N 4,861 867
North-East 17% 16%
Mid-West 28% 30%
South 29% 24%
West 26% 30%
_________________________________________________________________________________
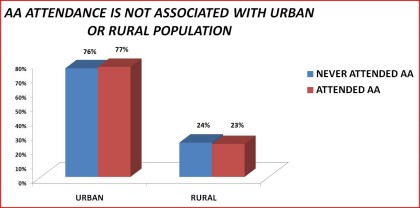
Urban / Rural Population
Table 13. Access to Alcoholics Anonymous by urban/rural population: 1992 National Longitudinal Alcohol Epidemiologic Suvey
______________________________________________________________________
Never Attended Ever Attended Significance
AA AA Level
______________________________________________________________________
N 4,861 867
Urban 76% 77% n.s.
Rural 24% 23%
Continuance in Alcoholics Anonymous
Alcoholics Anonymous Attendance
Table 14. Prior-to-past year DSM-IV alcohol abuse/dependence by continuance in Alcoholics Anonymous during the period prior to the past year: 1992 National Longitudinal Epidemiologic Survey
______________________________________________________________________
N 867
______________________________________________________________________
Continued in AA 34%
Discontinued AA 66%
______________________________________________________________________
Severity
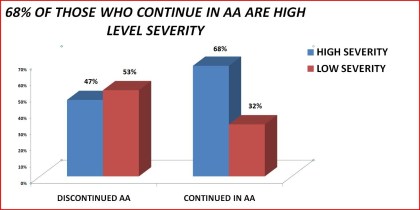
Figure 15. AA continuance by level of symptom severity

Table 15. Continuance in Alcoholics Anonymous by level of severity: 1992 National Longitudinal Alcohol Epidemiologic Survey
______________________________________________________________________
Discontinued Continued Significance
AA AA Level;
________________________________________________
N 568 299
High Severity 47% 68% < .0001
Low Severity 53% 32%
______________________________________________________________________
Prior Negative Life Events
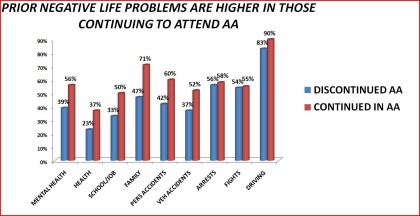 |
|
Figure 16. AA continuanxce by prior negative life events
|
Table 16. Continuance in Alcoholics Anonymous by prior negative life events: 1992 National Longitudinal Alcohol Epidemiologic Survey
Prior Drug Use
Table 17. Continuance in Alcoholics Anonymous by prior-to-past year drug use: 1992 National Longitudinal Alcohol Epidemiologic Survey
Gender
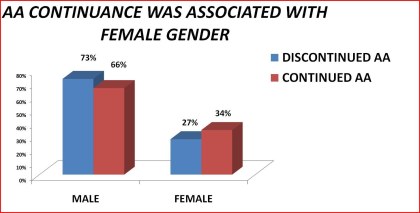 |
|
Figure 18. AA continuance by gender
|
Table 18. Continuance in Alcoholics Anonymous by gender: 1992 National Longitudinal Alcohol Epidemiologic Survey
Male 73% 66% < .05
Female 27% 34%
_____________________________________________________________________________________
Age
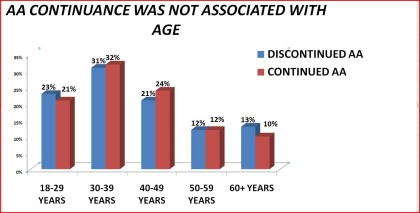 |
|
Figure 19. AA continuance by age group
|
Table 19. Continuance in Alcoholics Anonymous by age: 1992 National Longitudinal Alcohol Epidemiologic Survey
18-29 years 23% 21%
30-39 years 31% 32%
40-49 years 21% 24%
50-59 years 12% 12%
60+ years 13% 10%
____________________________________________________________________________________
18-29 years 23% 21% n.s.
30+ years 77% 29%
___________________________________________________________________________________
Race
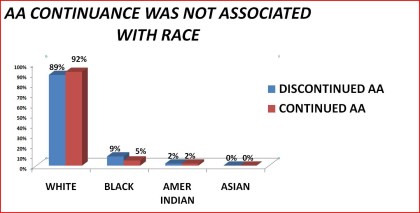 |
|
Figure 20. AA continuance by race
|
Table 20. Continuance in Alcoholics Anonymous by race: 1992 National Longitudinal Alcohol Epidemiologic Survey
____________________________________________________________________
Other 91% 95%
___________________________________________________________________________________
Marital Status
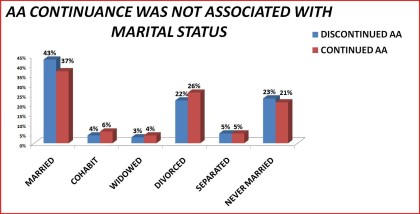 |
|
Figure 21. AA continuance by marital status
|
Table 21. Continuance in Alcoholics Anonymous by marital status: 1992 National Longitudinal Alcohol Epidemiologic Survey
______________________________________________________________________
Discontinued Continued Significance
AA AA Level
_______________________________________________________________________
N 568 299
Married 43% 37 %
Cohabit 4% 6%
Widowed 3% ` 4%
Divorced 22% 26%
Separated 5% 6%
Never Married 23% 21%
___________________________________________________________________
Divorced 22% 26% n.s.
Other 78% 74%
____________________________________________________________________
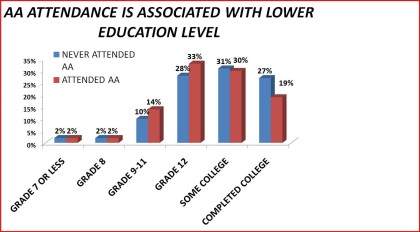
Education
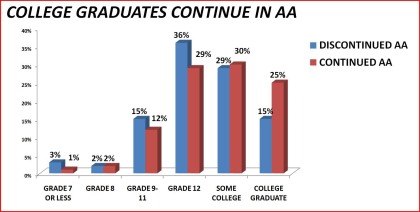
Figure 22. AA continuance by education level

Table 22. Continuance in Alcoholics Anonymous by education: 1992 National Longitudinal Alcohol Epidemiologic Survey
______________________________________________________________________
Discontinued Continued Significance
AA AA Level
_______________________________________________________________________
N 560 297
Grade 7 or less 3% 1%
Grade 8 2% 2%
Grade 9-11 15% 12%
Grade 12 36% 29%
Some College 29% 30%
College graduate 15% 25%
____________________________________________________________________
Some college or higher 45% 55% < .01
12 grade or lower 55% 45 %
____________________________________________________________________
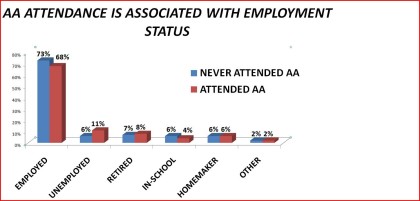
Employment Status
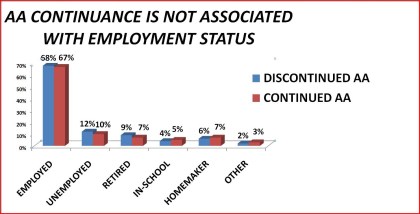 |
|
Figure 23. AA continuance by employment status
|
Table 23. Continuance in Alcoholics Anonymous by employment status: 1992 National Longitudinal Alcohol Epidemiologic Survey
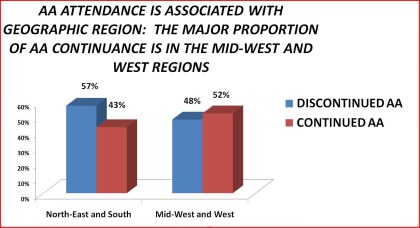
Table 24. Continuance in Alcoholics Anonymous by geographic region: 1992 National Longitudinal Alcohol Epidemiologic Survey
Mid-West and South 57% 48% < .05
North-East and West 43% 52%
_____________________________________________________________________________________
Urban / Rural Population
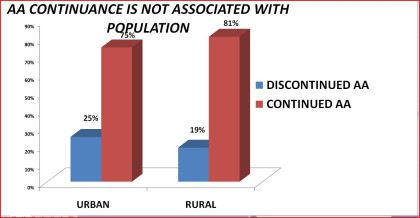
Table 25. Continuance in Alcoholics Anonymous by urban/rural population: 1992 National Longitudinal Alcohol Epidemiologic Survey
Age First Use of Alcohol
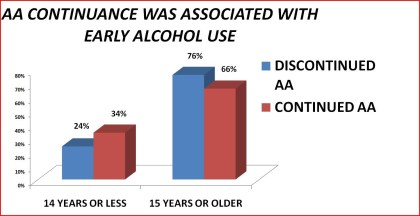
Table 26. Continuance in Alcoholics Anonymous by age of first use of alcohol: 1992 National Longitudinal Alcohol Epidemiologic Survey
14 years or less 24% 34% < .01
15 years and older 76% 66%
______________________________________________________________________________________